Customer relationships are the backbone of any successful business. Whether you’re a startup trying to acquire new clients or an enterprise managing a massive customer base, staying organized is crucial. That’s where CRM software comes in. But with so many options in the market, how do you decide which one is right for you? Understanding the different types of CRM software will help you make an informed choice and optimize your customer management strategy.
Every business talks about CRM, but why? Let’s break it down.
What is CRM Software? An Introduction
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software is a system designed to help businesses track, manage, and analyze customer interactions. It centralizes customer data, automates processes, and improves collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer service teams.
A CRM is not just a digital address book. It’s a strategic tool that helps businesses:
- Store and organize customer information
- Automate sales and marketing tasks
- Monitor customer interactions across multiple channels
- Analyze data to improve customer experiences and boost revenue
The CRM market has experienced significant growth, reflecting its importance across industries. As of 2023, the global CRM market was valued at approximately $71 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%, reaching around $129 billion by 2028.
Source: CRM Org.
Why businesses need CRM Software: Key Benefits
Implementing a CRM system offers a multitude of advantages:
Increased Sales Revenue: Businesses that utilize CRM systems are 86% more likely to exceed their sales targets compared to those that don’t.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: 53% of businesses report improved customer satisfaction and retention after adopting CRM tools.
Improved Efficiency: CRM software can reduce employee workload by automating repetitive tasks, saving employees 5 to 10 hours per week.
Better Data Management: Centralizing customer information ensures that data is organized, accessible, and actionable, leading to more informed decision-making.
Streamlined Communication: CRM systems facilitate communication within teams and with customers, making sure of consistency and clarity in interactions.
Types of CRM Software & Their Use Cases
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential tools that help businesses manage interactions with current and potential customers. Understanding the different types of CRM software is crucial for selecting a system that aligns with your organization’s goals and processes. Here is a comprehensive overview of the key types of CRM systems, their features, and suitable use cases.
1. Operational CRM
Operational CRM systems focus on automating and streamlining customer-facing processes. They are designed to support sales, marketing, and customer service operations by managing and automating workflows.
Key Features:
- Sales Automation: Manages the sales process, including lead generation, contact management, and order tracking.
- Marketing Automation: Facilitates campaign management, lead nurturing, and performance analytics.
- Service Automation: Handles customer service activities like issue tracking, case management, and service scheduling.
Use Cases:
Operational CRMs are ideal for organizations aiming to automate routine tasks, reduce manual workload, and enhance efficiency in customer interactions.
2. Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM systems are designed to analyze customer data to provide insights that inform strategic decisions. They help organizations understand customer behavior, preferences, and trends.
Key Features:
- Data Mining: Extracts patterns and relationships from large datasets.
- Customer Segmentation: Categorizes customers based on specific criteria for targeted marketing.
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasts customer behaviors and sales trends.
Use Cases:
Analytical CRMs are suitable for businesses that require in-depth data analysis to drive marketing strategies, sales forecasting, and customer retention initiatives.
3. Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM systems, also known as strategic CRMs, focus on facilitating communication and collaboration among various departments within an organization. They ensure that all teams have access to updated customer information.
Key Features:
- Interaction Management: Tracks all interactions between the company and customers across channels.
- Channel Management: Manages customer communication preferences and channels.
- Document Management: Organizes and shares documents like contracts and proposals.
Use Cases:
Collaborative CRMs are beneficial for organizations with multiple departments that interact with customers, ensuring a unified approach to customer relationship management.
4. Campaign Management CRM
Campaign Management CRM systems are specialized tools designed to handle various aspects of marketing campaigns. They assist in planning, executing, and analyzing marketing efforts across multiple channels.
Key Features:
- Campaign Planning: Assists in designing and scheduling marketing campaigns.
- Targeting and Segmentation: Identifies and segments target audiences for personalized messaging.
- Performance Analytics: Measures the effectiveness of campaigns through metrics and reports.
Use Cases:
These CRMs are ideal for marketing teams looking to manage complex campaigns, track performance, and optimize strategies based on data-driven insights.
Lett’s build smarter customer relationships together.
5. Strategic CRM
Strategic CRM systems are focused on long-term customer engagement and relationship building. They aim to align business processes with customer-centric strategies to foster loyalty and retention.
Key Features:
- Customer Experience Management: Monitors and enhances the overall customer journey.
- Loyalty Programs: Develops and manages initiatives to reward repeat customers.
- Feedback Collection: Gathers customer feedback for continuous improvement.
Use Cases:
Strategic CRMs are suitable for businesses aiming to build strong, long-term relationships with their customers by focusing on personalized experiences and satisfaction.
6. AI-Powered CRM
AI-powered CRM systems integrate artificial intelligence to automate processes, gain insights, and enhance customer interactions. They utilize machine learning and data analytics to provide predictive insights and personalized experiences.
Key Features:
- Predictive Lead Scoring: Identifies potential high-value customers.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Provides automated, real-time customer support.
- Sales Forecasting: Predicts future sales trends based on historical data.
Use Cases:
AI-powered CRMs are ideal for organizations looking to leverage advanced technologies to improve efficiency, customer satisfaction, and data-driven decision-making.
7. Industry-Specific CRM
Industry-specific CRM systems are tailored to meet the unique needs of particular industries. They offer customized features and workflows that align with industry-specific requirements.
Examples:
- Real Estate CRM: Manages property listings, client interactions, and transaction processes.
- Healthcare CRM: Handles patient information, appointment scheduling, and compliance with healthcare regulations.
- E-commerce CRM: Tracks customer purchases, manages inventory, and facilitates personalized marketing.
Use Cases:
These CRMs are best suited for businesses that require specialized functionalities to address industry-specific challenges and processes.
Industry-Specific CRM Solutions: Choosing the Right One
Different industries require different CRM functionalities. Some examples include:
- Healthcare: HIPAA-compliant CRM solutions that track patient interactions and manage appointments.
- Real Estate: Systems that handle property listings, client communication, and transaction histories.
- Financial Services: CRMs that monitor client portfolios, regulatory compliance, and risk assessment.
- Retail & E-commerce: Tools that focus on order tracking, customer preferences, and loyalty programs.
- Manufacturing: CRM solutions that coordinate supply chain operations and vendor relationships.
Selecting a CRM designed for your industry ensures that it aligns with your business’s specific needs.
Key CRM Features to Look For,
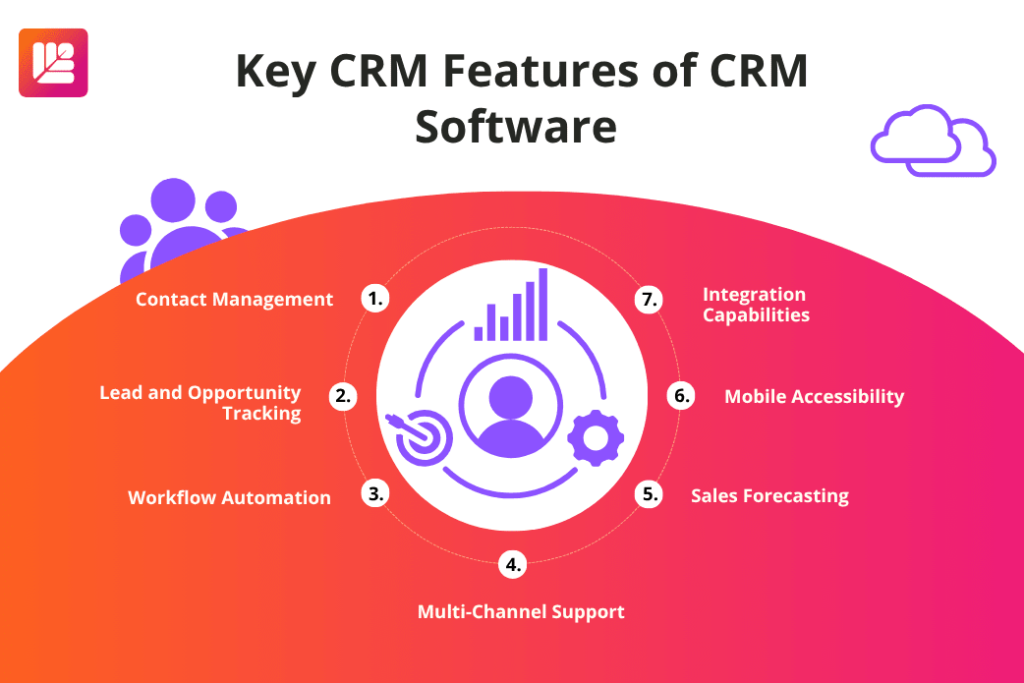
When evaluating CRM software, businesses should consider the following essential features:
- Contact Management: A centralized database for storing and organizing customer information.
- Lead and Opportunity Tracking: Tools to monitor sales prospects and customer interactions.
- Workflow Automation: Reduces manual tasks, improving productivity.
- Sales Forecasting: Provides data-driven insights into future sales performance.
- Multi-Channel Support: Enables communication through email, social media, phone, and live chat.
- Integration Capabilities: Connects with existing business tools like email marketing platforms, accounting software, and ERP systems.
- Mobile Accessibility: Allows sales and support teams to access CRM data on the go.
How to Choose the Best CRM for Your Business Needs
Finding the right CRM requires a careful assessment of your business goals and operational needs. Here’s how to make the right choice:
- Define Requirements: Identify the challenges you want the CRM to solve, such as customer engagement, data management, or automation.
- Assess Scalability: Make sure that the CRM can grow with your business and handle increasing data and users.
- Evaluate User-Friendliness: Choose a platform that is intuitive and easy for your team to adopt.
- Check Integration Options: A CRM should seamlessly integrate with your existing software ecosystem.
- Analyze Cost vs. ROI: Compare pricing plans and features to find a solution that offers the best value for your investment.
- Consider Customer Support: Opt for a CRM provider that offers strong technical support and training resources.
FAQs
- What is the best type of CRM for a small business?
-
For small businesses, an operational CRM with sales and marketing automation is often the best choice. It streamlines customer interactions and improves efficiency.
- Can a CRM integrate with existing business tools?
-
Yes, most modern CRMs integrate with email platforms, accounting software, customer support systems, and marketing automation tools.
- How much does CRM software cost?
-
CRM pricing varies based on features, users, and deployment type. Basic plans start at around $12–$25 per user per month, while enterprise solutions can exceed $100 per user per month.
- Is cloud-based CRM better than on-premise CRM?
-
Cloud-based CRMs offer flexibility, remote accessibility, and automatic updates, making them a popular choice. On-premise CRMs provide more control over data security but require higher maintenance costs.
- How long does it take to implement a CRM?
-
Implementation time depends on the complexity of the system. Basic setups take a few weeks, while enterprise-level integrations may take several months.
-
Previous Post
What Is Salesforce? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Post a comment Cancel reply
Related Posts
What Is Salesforce? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
Imagine running a business where every customer interaction, every sales lead, and every service request…
What Is CRM, and How Does It Work
In today’s business world, customer relationships are everything. Whether you’re running a small business or…
What Is Email Studio in Marketing Cloud
If you’ve ever tried running an email marketing campaign manually, you know the struggle. Crafting…
Salesforce Implementation Checklist 2025-26
Checklist to a Successful Salesforce Implementation for your Organization in 2023-24 Salesforce, a prominent CRM…