In today’s business world, customer relationships are everything. Whether you’re running a small business or managing a large enterprise, your success depends on how well you understand, engage with, and serve your customers. But as your business grows, keeping track of every interaction, follow-up, and customer need becomes overwhelming.
This is where Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come in. A CRM helps businesses organize customer data, automate workflows, improve communication, and boost sales efficiency.
But how exactly does CRM work? How can it benefit your business? And which CRM solution is the right fit? In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know, from CRM fundamentals to its future in AI-driven automation.
What is CRM?
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) is a strategy, process, and technology designed to manage all customer interactions in one place.
In the past, businesses relied on handwritten notesImplementing a CRM system is more, spreadsheets, and disconnected databases to track customer relationships. However, as companies scaled, these methods became inefficient. Today’s modern CRM systems centralize customer data, automate repetitive tasks, and provide real-time insights to help businesses make informed decisions. To implement such systems effectively, many organizations choose to hire Salesforce consultants or experienced CRM specialists who understand both technology and business processes.
Key Purpose of a CRM
Stores and organizes customer details, interactions, and purchase history
- Automates workflows for sales, marketing, and customer support
- Provides reports and analytics to track business performance
- Improves collaboration between teams by offering a 360-degree view of every customer
With CRM, businesses can move beyond guesswork and make data-driven decisions to improve customer experience and maximize revenue.
What does a CRM do?
A CRM system acts as the nerve center of your customer interactions. It tracks and manages relationships at every stage, from lead generation to post-sale customer support.
1. Centralized Customer Data
Imagine you’re a sales representative. A customer calls, but you don’t have their purchase history or previous complaints readily available. With CRM, you can pull up their entire profile in seconds, previous interactions, orders, service requests, and even social media mentions.
2. Sales Process Automation
Sales teams waste hours on manual data entry, scheduling follow-ups, and tracking deals. A CRM system automates these processes, allowing reps to focus on closing deals rather than updating spreadsheets. For example, if a lead downloads a product brochure, the CRM can automatically assign a sales rep, schedule a follow-up call, and send a personalized email, all without manual intervention.
3. Marketing Campaign Optimization
CRMs help marketing teams segment customers based on behavior, preferences, and demographics. This provides personalized email campaigns, automated lead nurturing sequences, and performance tracking of ads and promotions. Advanced setups often include Salesforce Marketing Cloud implementation services to maximize campaign effectiveness.
4. Customer Support Management
If a customer submits a complaint, the CRM ensures support agents have full context, previous issues, past purchases, and communication history, so they can resolve problems faster and more effectively.
5. Data-driven Decision Making
A CRM provides real-time analytics on sales trends, marketing performance, and customer satisfaction levels, allowing businesses to identify weaknesses and optimize strategies. In short, CRM turns scattered information into structured, actionable insights, empowering businesses to build stronger relationships.
How does CRM work?
CRM software acts as a central hub that connects different business functions, sales, marketing, and customer service, to create a cohesive customer journey.

Step 1: Lead Capture & Organization
When a potential customer interacts with your business, whether through a website form, social media, or email, the CRM automatically records their details and assigns a lead score based on their level of interest. If a visitor downloads a whitepaper and requests a demo, the CRM assigns them a high-priority lead score and notifies the sales team
Step 2: Sales Pipeline Management
Sales teams use the CRM to track leads through different stages: Initial contact → Product demo → Proposal sent → Deal closed. The CRM sends reminders for follow-ups, schedules meetings, and logs communications
Step 3: Customer Purchase & Onboarding
Once a deal is closed, the CRM updates the customer’s status and hands off details to customer support for onboarding and post-sale engagement.
Step 4: Customer Retention & Upselling
A CRM helps businesses predict customer needs, track satisfaction levels, and offer upsell or renewal opportunities at the right time. By automating these processes, businesses can streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve customer engagement.
Does your business need a CRM?
If your business deals with a growing number of customers, managing relationships manually becomes unsustainable. In such cases, partnering with a reliable offshore Salesforce development services can help scale CRM operations efficiently.
Consider these key indicators that suggest you need a CRM:
- You struggle to keep track of customer interactions across different platforms.
- Sales teams miss follow-ups due to a lack of structured workflow.
- Marketing campaigns feel generic and untargeted.
- Customer service suffers from slow response times and incomplete information.
- Business decisions are based on gut feeling rather than data-driven insights.
A CRM helps businesses address these challenges by organizing data, automating workflows, and improving communication across teams.
Key Components of a CRM System
A CRM is not just a contact database. It consists of multiple tools working together:
1. Contact & Lead Management
- Store customer details, purchase history, and communication logs
- Assign lead scores based on engagement and sales readiness
2. Sales Automation
- Tracks deals, contracts, and proposals
- Automates reminders for follow-ups and meetings
3. Marketing Automation
- Segmentation for targeted campaigns
- Tracks customer interactions with email, social media, and websites
4. Customer Service Management
- Support ticketing system to manage queries and complaints
- AI chatbots Service for instant assistance
5. Reporting & Analytics
- Custom dashboards for real-time business performance insights
- Predictive analytics to forecast future sales trends
Types of CRM Technology
Not all CRM systems are the same. The right choice depends on business needs and objectives.
1. Operational CRM
Focuses on automating sales, marketing, and customer support processes to improve efficiency. Example: Salesforce Sales Cloud
2. Analytical CRM
Uses data analytics, AI, and reporting tools to provide insights into customer behavior.
Example: SAP CRM, Oracle CRM
3. Collaborative CRM
Improves internal communication between teams by integrating data across departments.
Example: Microsoft Dynamics 365
Benefits of using a CRM: Why businesses invest in CRM Solutions
A CRM system improves efficiency, increases revenue, and enhances customer relationships. Key benefits of using CRM Solutions include:
1. Stronger Customer Relationships
By tracking past interactions, businesses can personalize communication and build trust.
2. Increased Sales Efficiency
Automated follow-ups and sales tracking help sales teams close more deals with less effort.
3. Improved Marketing ROI
CRM-powered segmentation ensures that marketing messages reach the right audience at the right time.
4. Better Collaboration Across Teams
A centralized platform keeps sales, marketing, and support teams aligned.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Real-time insights help businesses adjust strategies and stay ahead of market trends.
How to choose the right CRM for your business?
When evaluating CRM options, consider:
- Cloud vs. On-Premises CRM: Cloud solutions offer flexibility, while on-premises CRMs provide more control.
- Customization Needs: Does the CRM allow integrations with your existing tools?
- User Experience: An intuitive interface ensures smooth adoption by your team.
Salesforce remains one of the most preferred CRM solutions due to its extensive features and AI-driven insights.
Who can use a CRM?
CRMs are used by a wide range of businesses, including:
- Startups and small businesses to manage growing customer bases
- Enterprises to optimize large-scale sales operations
- E-commerce stores for personalized marketing
- B2B companies for lead tracking and pipeline management
CRM Implementation: Steps and Best Practices
Implementing a CRM system is more than just adopting software, it’s about aligning technology with business processes. Many organizations rely on Salesforce migration services to move data securely and ensure a smooth transition from legacy systems.
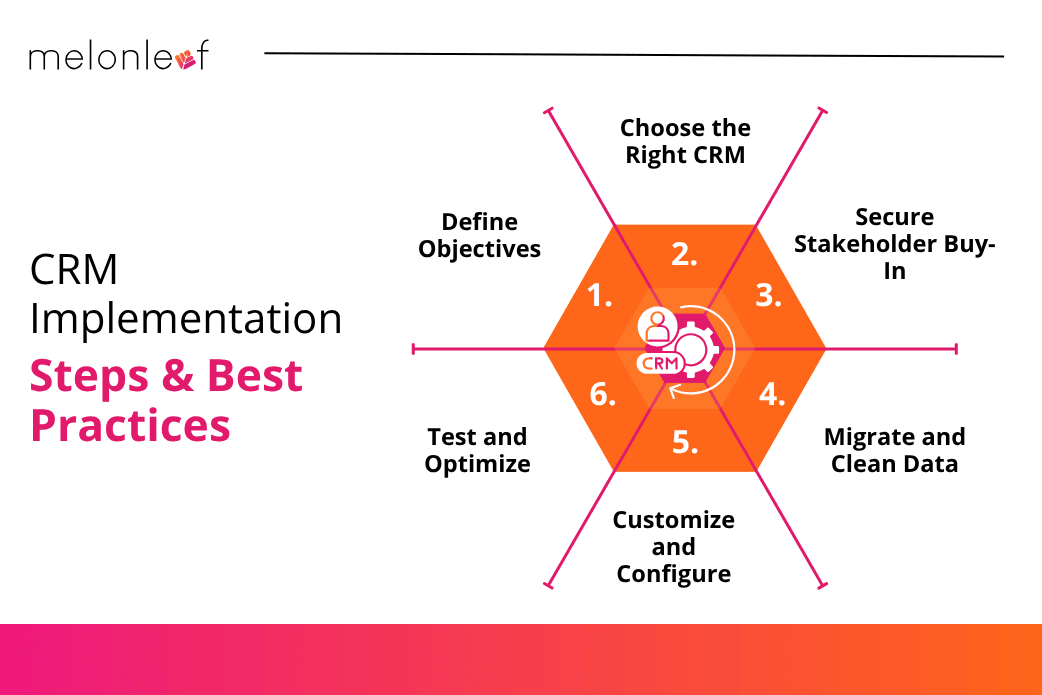
Steps for CRM Implementation
- Define Objectives: Identify key business needs like sales automation or customer service improvement.
- Choose the Right CRM: Consider scalability, features, and integration with existing tools.
- Secure Stakeholder Buy-In: Leadership and team support are critical for success.
- Migrate and Clean Data: Organize and standardize customer data before transferring it.
- Customize and Configure: Adapt workflows, dashboards, and automation to fit business processes.
- Train and Support Users: Conduct training sessions and provide continuous support.
- Test and Optimize: Roll out the system in phases, gather feedback, and adjust accordingly.
Best Practices for CRM Implementation,
- Implement gradually rather than all at once.
- Focus on automation without overcomplicating processes.
- Encourage adoption through incentives and feedback.
The Evolution of CRM Systems
CRM systems have come a long way from manual record-keeping to AI-driven platforms that actively drive customer engagement. Understanding this evolution highlights how businesses can use CRM to stay competitive.
Key Stages in CRM Evolution
- Pre-Digital Era: Businesses relied on paper-based customer records.
- 1980s–1990s: Early CRM Software: Databases and sales force automation tools emerged.
- 2000s: Cloud-Based CRM: Salesforce introduced the SaaS model, making CRM more accessible.
- 2010s: AI and Automation: Marketing automation, chatbots, and analytics became standard.
- 2020s and Beyond: AI, voice-enabled CRM, and blockchain are shaping the future.
Modern CRM has transformed from a simple database into an intelligent, predictive business tool.
The Future of CRM Technology
The future of CRM will focus on smarter, more predictive, and highly personalized customer interactions. Businesses that embrace emerging trends will gain a competitive advantage.
Emerging Trends in CRM
- AI and Predictive Analytics: CRM will forecast customer behavior and automate responses.
- Hyper-Personalization: AI-driven recommendations will create tailored customer experiences.
- Voice and Conversational CRM: Integration with virtual assistants for hands-free interactions.
- No-Code Customization: Businesses will easily modify CRM features without technical expertise.
- Blockchain for Security: Decentralized records will enhance data privacy and trust.
CRM is evolving into an intelligent system that not only stores data but actively improves customer engagement and decision-making.
Wrap Up
CRM is more than a tool, it’s a strategic investment that enhances customer relationships, streamlines sales, and drives business growth. Choosing the right CRM and implementing it correctly provides long-term success.
For businesses looking to integrate CRM effectively, Melonleaf Consulting as the top Salesforce Consultant offers expert guidance in selecting, implementing, and optimizing CRM solutions tailored to specific business needs.